Nucleus accumbens
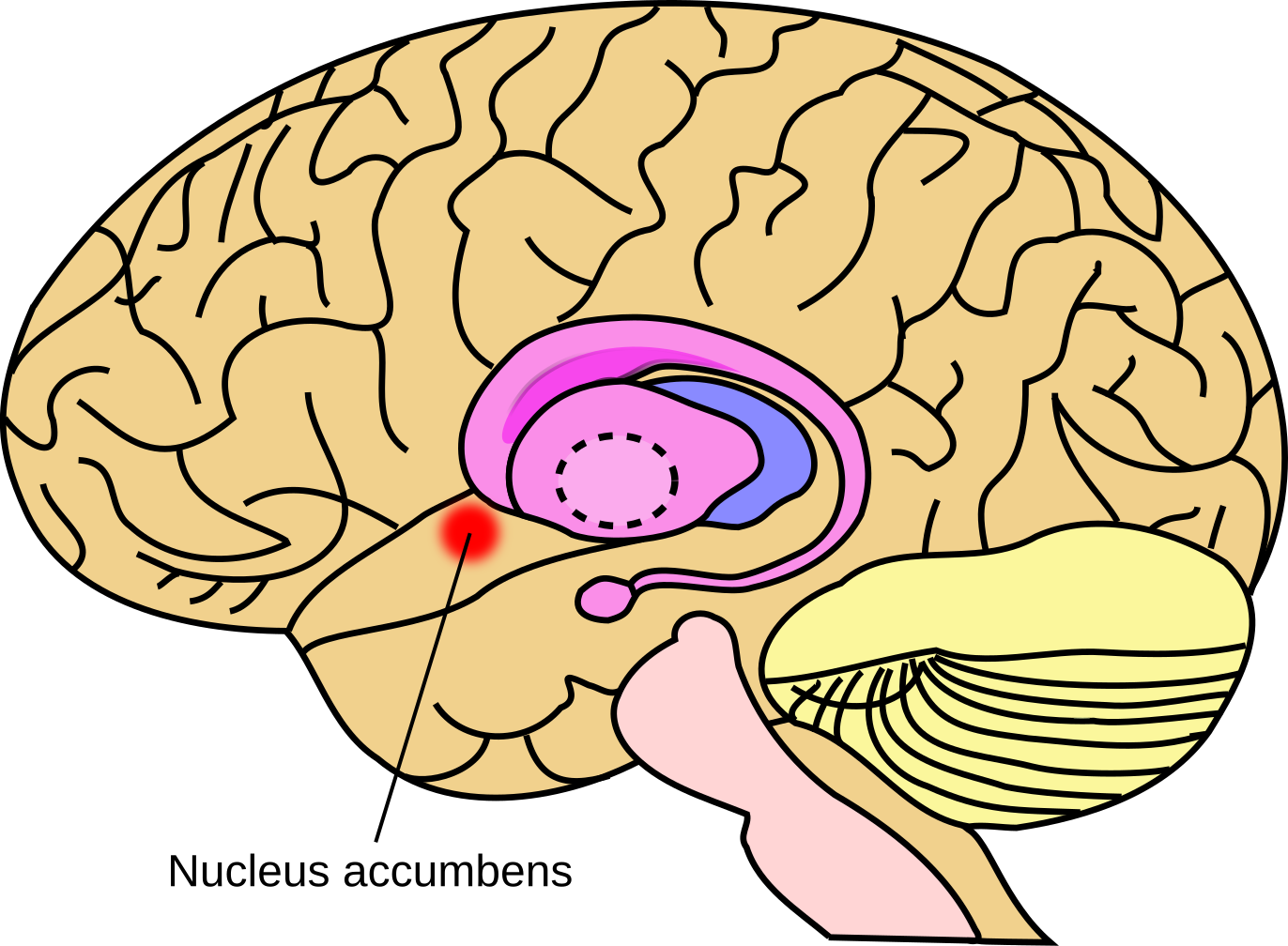
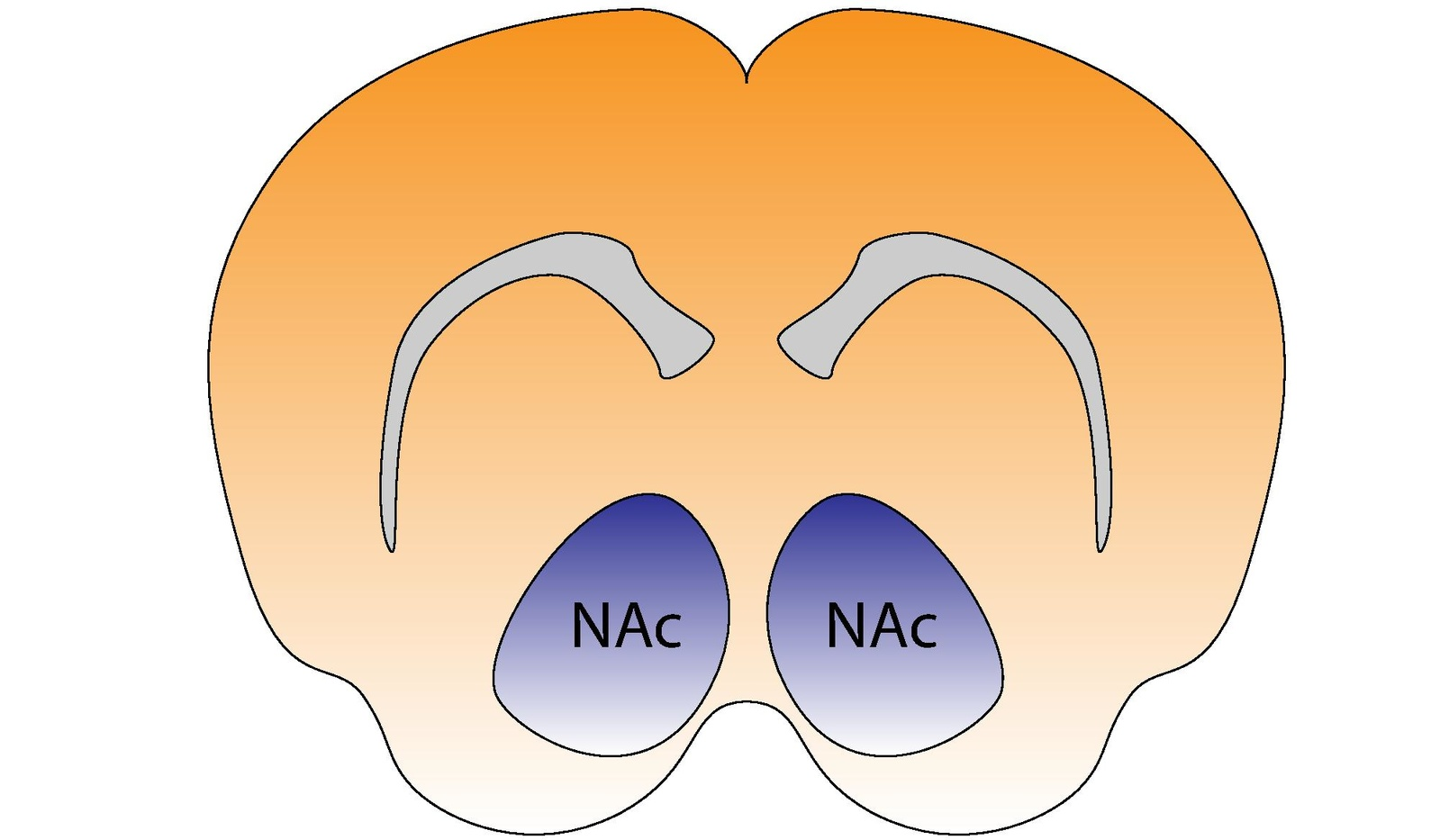
The nucleus accumbens core (NAcc core) is the inner substructure of the nucleus accumbens.
Location: The nucleus accumbens core is part of the ventral striatum, located within the basal ganglia. Cell types: The core of the NAcc is made up mainly of medium spiny neurons containing mainly D1-type or D2-type dopamine receptors. The D1-type medium spiny neurons mediate reward-related cognitive processes, whereas the D2-type medium spiny neurons mediate aversion-related cognition. The neurons in the core, as compared to the neurons in the shell, have an increased density of dendritic spines, branch segments, and terminal segments. From the core, the neurons project to other sub-cortical areas such as the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra. GABA is one of the main neurotransmitters in the NAcc, and GABA receptors are also abundant.
Function: The nucleus accumbens core is involved in the cognitive processing of motor function related to reward and reinforcement and the regulation of slow-wave sleep. Specifically, the core encodes new motor programs which facilitate the acquisition of a given reward in the future. The indirect pathway (i.e., D2-type) neurons in the NAcc core which co-express adenosine A2A receptors activation-dependently promote slow-wave sleep. The NAcc core has also been shown to mediate general Pavlovian-instrumental transfer, a phenomenon in which a classically conditioned stimulus modifies operant behavior.